Unique Unaudited Accounts Deferred Tax Assets And Liabilities Examples
Income Taxes and Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities 1.
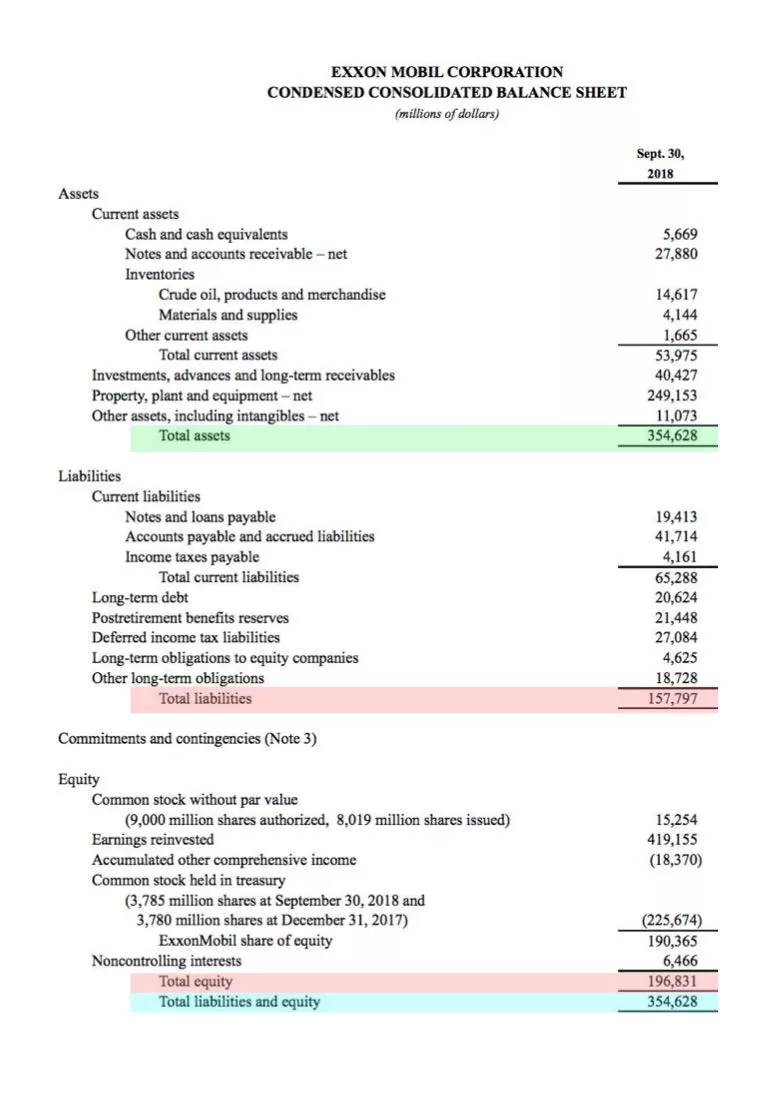
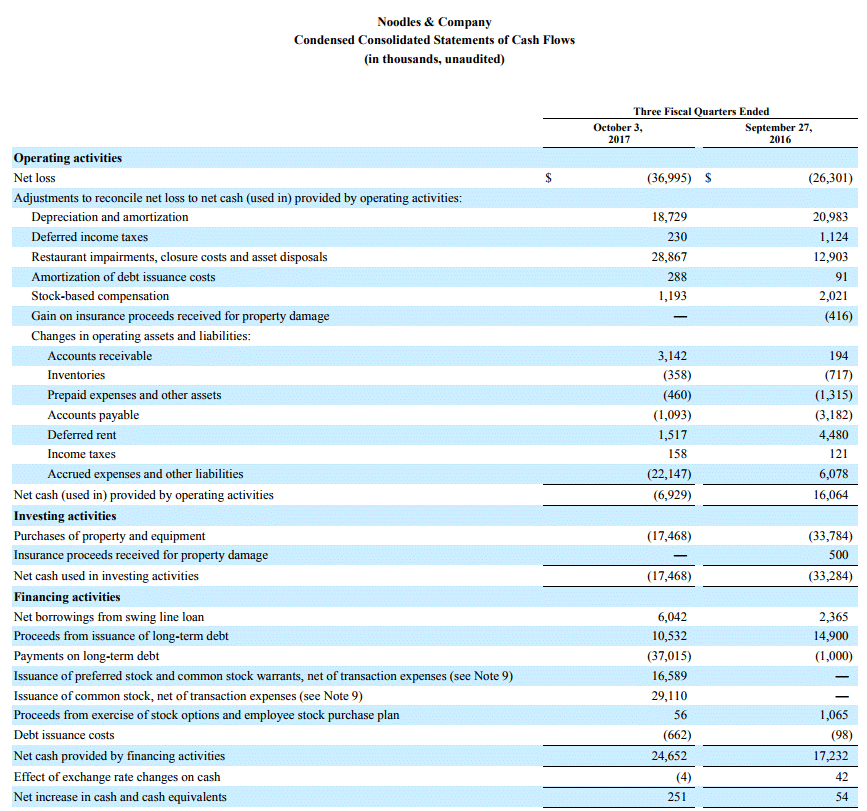
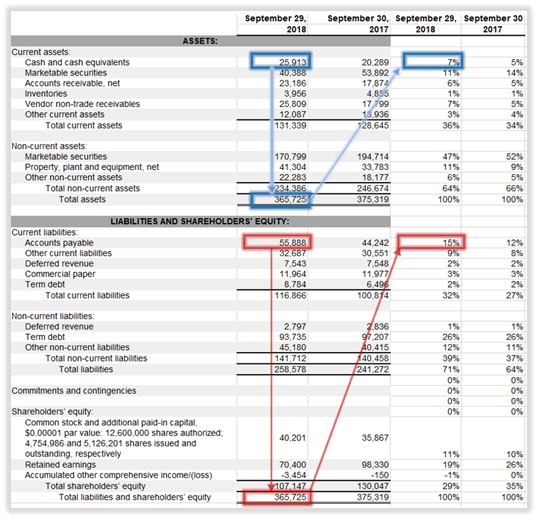
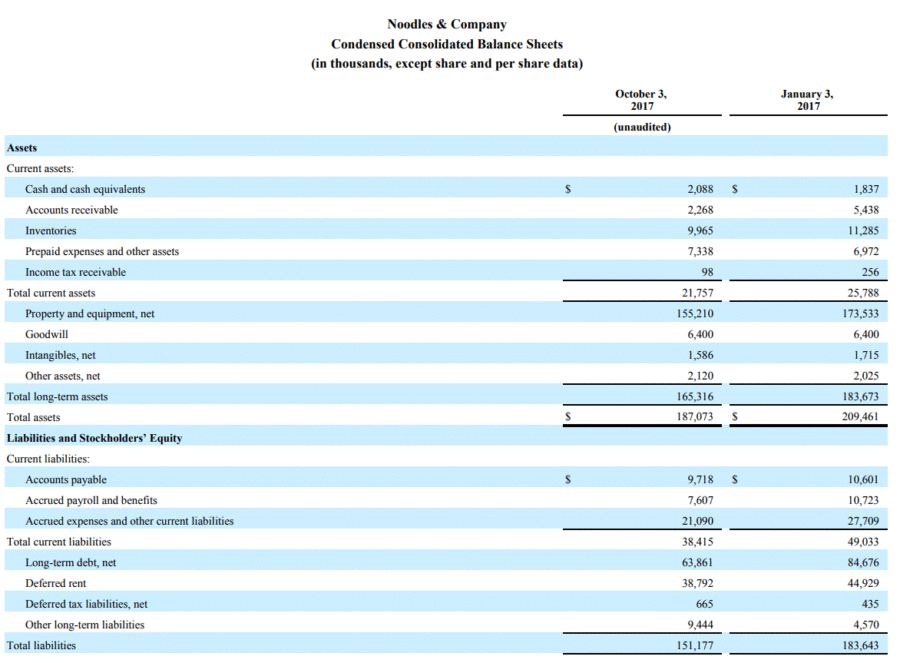
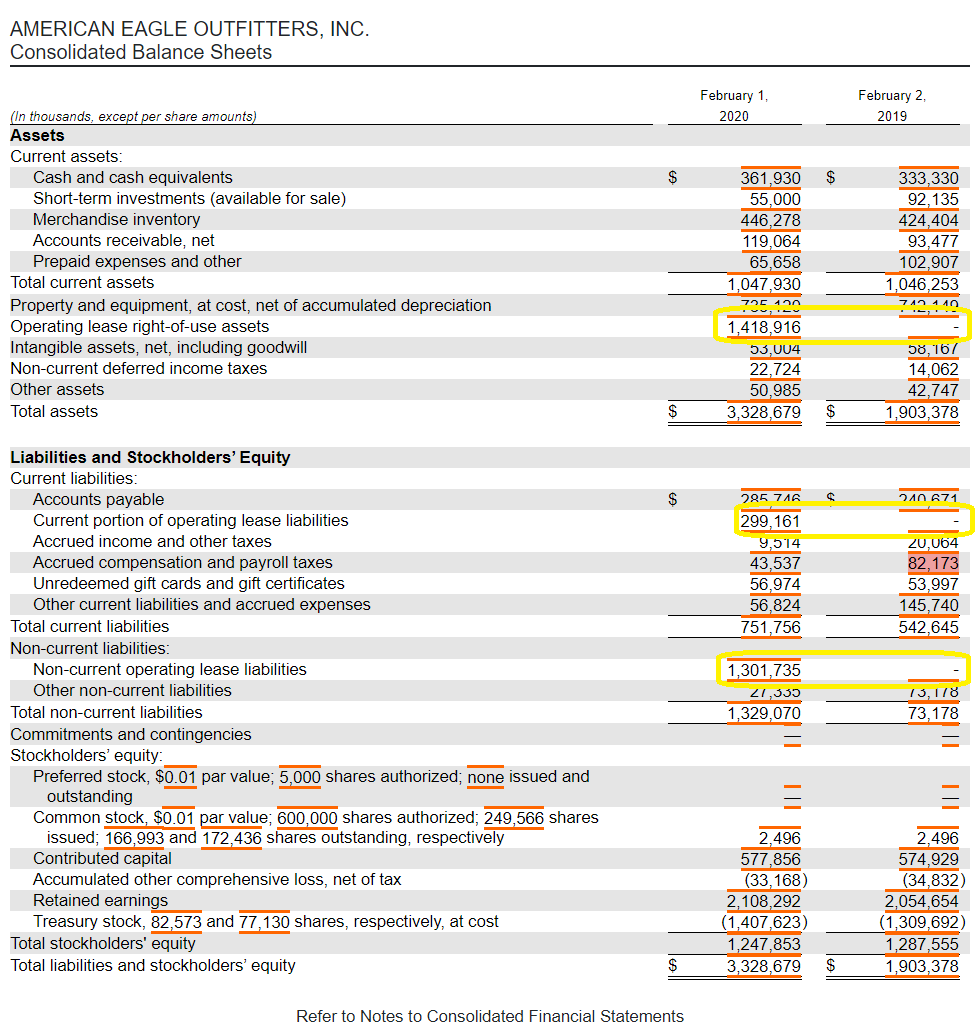
Unaudited accounts deferred tax assets and liabilities examples. Right-of-use assets and lease liabilities. B a deferred tax liability for temporary differences that will increase taxable profit taxable temporary differences. Total deferred tax liabilities 3847 3442 34143 Net deferred tax assets 18294 19378 162355 23.
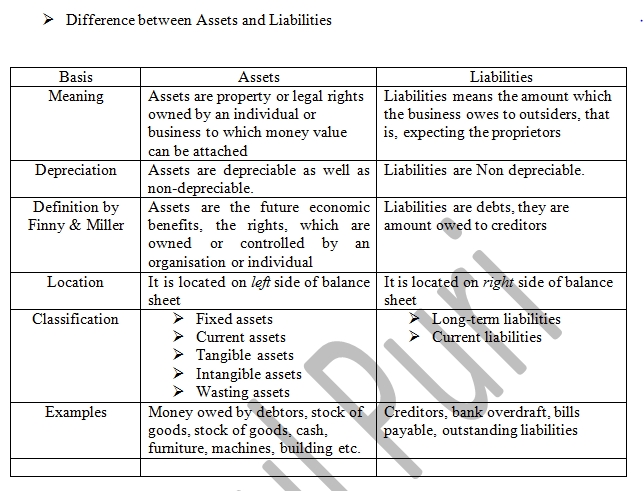
Deferred tax asset liability is booked in accounts to neutralize those temporarytiming differences arising due to accounting policies followed by the business and the treatments allowed under tax laws. In the first case deferred tax expense account is debited and the deferred tax liability account is credited. What are deferred tax assets and liabilities.
Depending upon nature of temporary differences following two types of deferred tax provision can be recognized. Because a change in tax law is accounted for in the period of enactment. Warranties Accounts receivable that are uncollectible Options expensing Leases Net operating losses Depreciable assets.
For example an expense which is not allowable for tax purposes but is included in the financial statements would create a situation where the taxable income is greater than the accounting income resulting is an higher tax expense. Here are some transactions that generate deferred tax asset and liability balances. Step 3 Identify and calculate any exempt temporary differences Step 4 Identify the relevant tax rate and apply this to calculate deferred tax Step 5 Calculate the amount of any deferred tax asset that can be recognised Step 6.
Significant components of the Companies deferred tax assets and liabilities for the years ended March 31 2016 and 2015 are as follows. Deferred tax assets and liabilities exist because the income on the tax return is different than income in the accounting records income per book. The company records 240 800 30 as a deferred.
Entity accrues revenue which will be taxable when the cash is collected a fixed asset is depreciated faster for tax purposes than for accounting purposes. Recognition of equal amounts of deferred tax assets and liabilities an entity would in the absence of the exemption provided by paragraphs 15 and 24 recognise the resulting deferred tax liability or asset and adjust the carrying amount of the asset or liability by the same amount. - Item of plant purchased for 1000 - Accounting depreciation Straight Line over life of 20 years - Tax depreciation Diminishing Value at 30 pa - Profit before depreciation 500 every year - Tax rate 30 Deferred Tax in Profit and Loss Account After One Year.
/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-01-3998c75d45bb4811ad235ef4eaf17593.jpg)
/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-01-3998c75d45bb4811ad235ef4eaf17593.jpg)
/phpdQXsCD-204ee8d463444c6c90f775fd179810f3.png)
/phpdQXsCD-204ee8d463444c6c90f775fd179810f3.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Other_Current_Assets_OCA_Dec_2020-01-1ef8bd75eff345e7ac48ba70fb718619.jpg)